Lorentz Distribution
 The Lorentz distribution is named after Hendrik Lorentz) is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among mathematicians as the Cauchy distribution (after Augustin Cauchy).
The Lorentz distribution is named after Hendrik Lorentz) is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among mathematicians as the Cauchy distribution (after Augustin Cauchy).
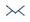
The distribution is used frequently to simulate the response profiles of systems to applied power. When applied as a Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF), a response profile is described with maximum efficiency in mid-ranges and reducing efficiency as power approaches minimum or maximum (see example).
Cumulative Distribution Function
where x is the power input, n is the system's nominal power input and w is the function's mathematical 'width'.
The width of the function can be adjusted to alter the response profile to fit the requirements of the particular system. It can also be changed programmatically to alter system characteristics in response to changes in operating conditions. For example, the response profile of the fusion reactor's main containment field generators changes in response to operating temperature. The temperature changes are reflected by altering the width of the CDF used in the field generator component.
Modifier
The output of the CDF is usually modified to meet the system's expected operating range. Typically, the modifier will be the expected maximum of the system's operating range.
Probability Density Function
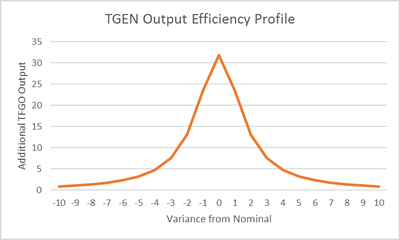 When represented as a Probability Density Function (PDF), the distribution described the efficiency profile of the same system.
When represented as a Probability Density Function (PDF), the distribution described the efficiency profile of the same system.